‘PM’ or particulate matter, also known as particle pollution is the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
It’s estimated that air pollution is linked to 43,000 deaths per year in the UK. Worldwide, at least 7 million people die each year from exposure to air pollution, with 91% of the worldwide population living in locations where the air quality exceeded the World Health Organisations (WHO) air pollution guidelines.
These guidelines state that that annual average concentrations of PM2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m3 and PM10 should not exceed 15 µg/m3 (both for 24-hour periods). According to the WHO, ‘fine particulate matter at PM2.5 can penetrate through the lungs and further enter the body through the blood stream, affecting all major organs’. Exposure to dust at PM2.5 can cause serious disease to the respiratory system, such as lung cancer and COPD, and also can effect cardiovascular diseases, such as a stroke.
The image below demonstrates PM2.5 and PM10 size in comparison to a single human hair and a grain of sand.
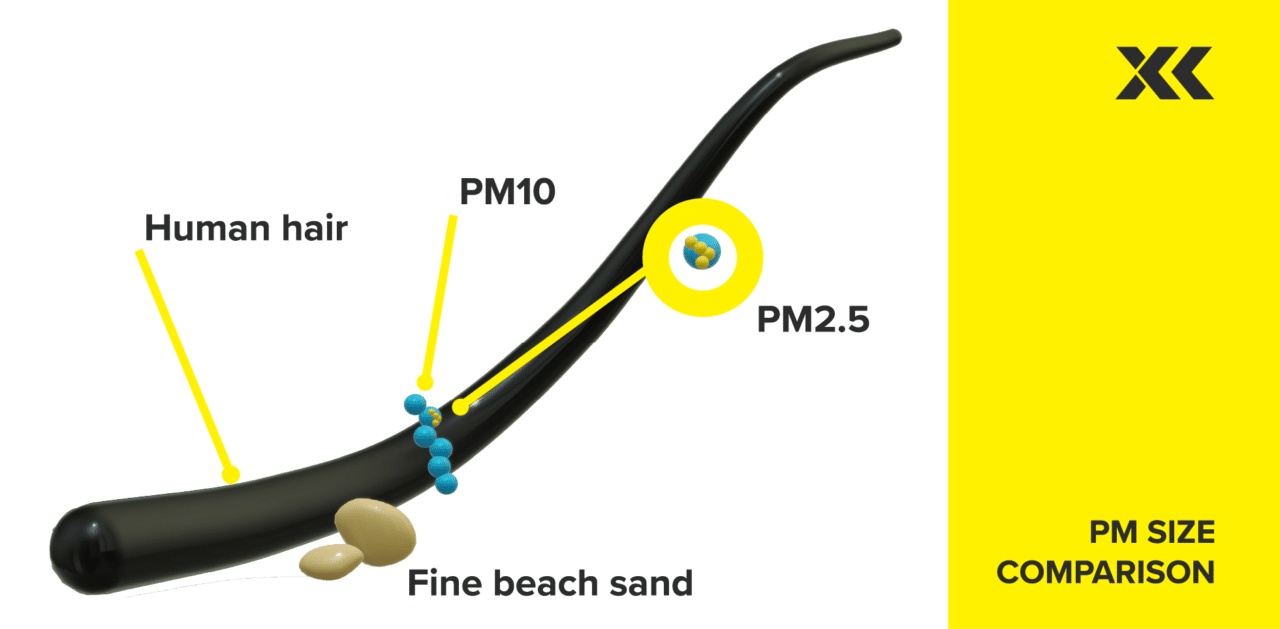
The Department for Environment Food & Rural Affairs (DEFRA), the UK government ministerial department for environment protection, have also highlighted the severity of exposure to air pollution. This growing concern for the UK government estimated in 2010 that the cost of health impacts of air pollution was likely to exceed estimates of £8bn to £20bn.
Although between 2005 and 2022, the UK’s PM2.5 emissions decreased by 41%, emission levels have been relatively steady with small annual fluctuations in the last decade. Industrial combustion is a major source of PM emissions, as well as emissions from industrial production also playing a major part, which can be linked to heavy-dust industry where hazardous particulates can become airborne. Despite some reductions in PM emissions, the threat still very much remains.

A solution to this is real-time dust monitoring. Real-time particulate monitoring allows people in heavy dust loading environments, including industrial applications, to not only understand, but alert them instantaneously when they are exposed to dangerous levels of air pollution. For example, our AIR XD Dust Monitor can alert people in real-time when legislative levels of µg/m3 are breached, over a time-weighted average (TWA) 8-hour period, for both PM2.5 and PM10.
This technology not only offers a simple solution to individuals at high risk of exposure to air pollution by providing instant alerts, but also can help to prevent exposure in the future, as at-risk individuals can learn exactly when and where exposure to air pollution is highest and will likely occur. Thanks to real-time monitoring, both in the UK and Worldwide, we can reduce exposure to air pollution.
We’re living through an air pollution emergency. One that’s already claiming thousands of lives and costing billions of pounds. And that news shouldn’t come as a surprise.
We wrote in a recent blog, The threat from particulates: It gets worse about an American academic study: “Long-Term Exposure to Fine Particulate Matter, Residential Proximity to Major Roads and Measures of Brain Structure.”
The report clearly shows the risks that people living over extended periods near busy main roads face from fine dust that causes respiratory diseases, results in brain atrophy (brain shrinkage) and leads to an increased risk of stroke and other disease.
Another academic paper, ‘Air Pollution and Noncommunicable Diseases’ suggests that air pollution may be damaging ‘every organ in the body.’
Unfortunately there was nothing ‘academic’ about the consequences of particulate inhalation for nine year old Ella Kissi-Debrah, whose death in 2013 was caused by ‘acute respiratory failure, severe asthma and air pollution exposure’.
“The whole of Ella’s life was lived in close proximity to highly polluting roads. I have no difficulty in concluding that her personal exposure to nitrogen dioxide and PM was very high,” stated the coroner.
And the really sad thing about Ella and her family’s suffering?
Is that it’s far from unusual.
According to the World Health Organisation, air pollution is the “new tobacco”, killing 7 million people a year and harming billions more.
“No one, rich or poor, can escape air pollution. It is a silent public health emergency.” Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, the WHO’s director general.
More than nine in ten people breathe toxic air and 300 million live where toxic fumes are six times above international guidelines and the health impacts are profound – especially for children.

So what’s going on? How is it possible that so many people suffer so much through filthy, contaminated air?
A rush for profits? For progress? For economic advancement? A lack of technology? Insufficient knowledge? Clarity of thought? Understanding? Will? A short-termism that prioritised wealth over health?
In truth it’s all these factors and more. Reasons, more often excuses, that in the not so distant future people will look back at in horror. A situation where people simply won’t believe that things were allowed to get so bad and stay so bad for so long.
Thankfully, though belatedly, the weight of detailed research, visible interventions from the likes of WHO, an increasingly active green movement and high profile tragedies such as the death of Ella Kissi-Debrah are seeing attention at last turning to the issue of air pollution and how best to tackle it.
So much so that the language of particulates and respiratory health is even entering mainstream use. The government responded to Ella Kissi-Debrah’s death with, “We are delivering a £3.8 billion plan to clean up transport and tackle NO2 pollution, and going further in protecting communities from air pollution, particularly PM2.5 pollution, which we know is particularly harmful to people’s health.’
Which is great.
But while a public recognition of the issue and an ability to deploy the right words in addressing the issue is a positive sign, it’s the ability of governments and industry to actually do something about air pollution that really matters. Action that all of us will be judged on in the future.

Signs are mixed. For example, despite the UK Government’s recognition that we all need to be protected from toxic air, and despite pledging funds to fight that cause, it has so far voted against proposals to put WHO pollution limits into UK law, arguing that they’re ‘uneconomical.’
‘Were you part of the problem or part of the solution?’ we’ll all be asked in the not too distant future.
Which is why we do what we do here at Trolex – to be a very proud and purposeful part of the solution.
Enquire today about our new AIR XD Dust Monitor and XD ONE Portable Dust Monitor in our real-time dust monitoring range – accurate, simple to use, easy to maintain, real-time particulate detection technology that keeps people safe.