‘PM’ or particulate matter, also known as particle pollution is the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air.
It’s estimated that air pollution is linked to 43,000 deaths per year in the UK. Worldwide, at least 7 million people die each year from exposure to air pollution, with 91% of the worldwide population living in locations where the air quality exceeded the World Health Organisations (WHO) air pollution guidelines.
These guidelines state that that annual average concentrations of PM2.5 should not exceed 5 µg/m3 and PM10 should not exceed 15 µg/m3 (both for 24-hour periods). According to the WHO, ‘fine particulate matter at PM2.5 can penetrate through the lungs and further enter the body through the blood stream, affecting all major organs’. Exposure to dust at PM2.5 can cause serious disease to the respiratory system, such as lung cancer and COPD, and also can effect cardiovascular diseases, such as a stroke.
The image below demonstrates PM2.5 and PM10 size in comparison to a single human hair and a grain of sand.
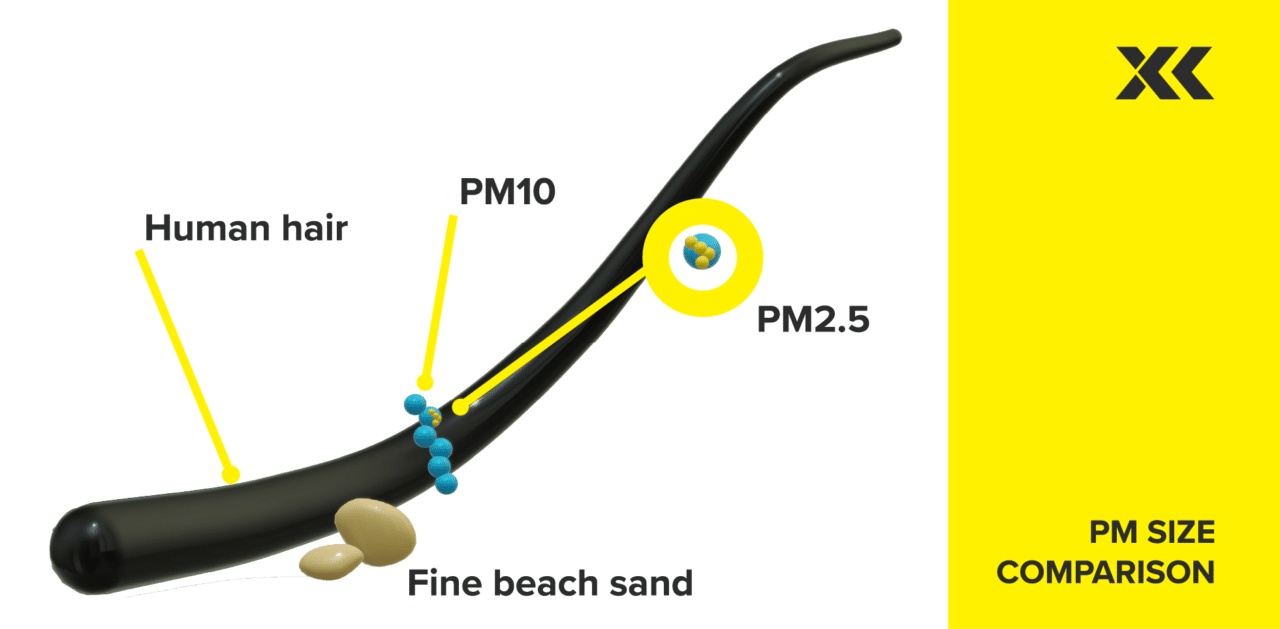
The Department for Environment Food & Rural Affairs (DEFRA), the UK government ministerial department for environment protection, have also highlighted the severity of exposure to air pollution. This growing concern for the UK government estimated in 2010 that the cost of health impacts of air pollution was likely to exceed estimates of £8bn to £20bn.
Although between 2005 and 2022, the UK’s PM2.5 emissions decreased by 41%, emission levels have been relatively steady with small annual fluctuations in the last decade. Industrial combustion is a major source of PM emissions, as well as emissions from industrial production also playing a major part, which can be linked to heavy-dust industry where hazardous particulates can become airborne. Despite some reductions in PM emissions, the threat still very much remains.

A solution to this is real-time dust monitoring. Real-time particulate monitoring allows people in heavy dust loading environments, including industrial applications, to not only understand, but alert them instantaneously when they are exposed to dangerous levels of air pollution. For example, our AIR XD Dust Monitor can alert people in real-time when legislative levels of µg/m3 are breached, over a time-weighted average (TWA) 8-hour period, for both PM2.5 and PM10.
This technology not only offers a simple solution to individuals at high risk of exposure to air pollution by providing instant alerts, but also can help to prevent exposure in the future, as at-risk individuals can learn exactly when and where exposure to air pollution is highest and will likely occur. Thanks to real-time monitoring, both in the UK and Worldwide, we can reduce exposure to air pollution.

Launched in 2022, the AIR XS Silica Monitor isn’t like other silica monitors on the market. If you’ve been in the Health and Safety space, it’s likely you’ll know about Optical Particle Counter (OPC), also known as “light-scattering”; but our patented AIR XS isn’t just another OPC.
Unlike traditional Optical Particle Counters (OPCs) that rely on light scattering and interruptions to deduce particle size and quantity, the patented Optical Refraction Technology (ORT) used in the AIR XS shines a laser through each particle, capturing its refraction on multiple sensors.
In our blog below, we reference Pink Floyd’s 1973 album Dark Side of the Moon to explain one way to how ORT works. It’s not exact by any means but the refraction of the light coming out of the prism shows an example of how light refracts, similar to a crystalline particle.